
PPCP (Polypropylene Copolymer) is a high-performance thermoplastic material widely used in industries that require strength, toughness, and durability. At Swami Polymers, we supply premium-grade PPCP materials to support manufacturing sectors such as automotive, household products, appliance parts, industrial components, and more.
Compared to normal PP (Polypropylene Homopolymer), PPCP offers better impact resistance, improved flexibility, and higher crack resistance, especially in low-temperature environments. This makes it one of the most reliable materials for long-lasting applications.
What Is PPCP (Polypropylene Copolymer)?
PPCP is produced by combining propylene monomers with ethylene monomers, resulting in a stronger and more impact-resistant polymer structure. Due to the added ethylene content, PPCP becomes tougher and more flexible than standard PP.
Key Characteristics of PPCP
- Excellent impact strength (better than PP)
- High chemical resistance
- Good low-temperature performance
- High durability and stress-crack resistance
- Can be easily injection-molded
- Lightweight but strong
- Recyclable material
Because of these properties, PPCP is heavily used in industries requiring rigid yet tough parts.
How PPCP Is Manufactured
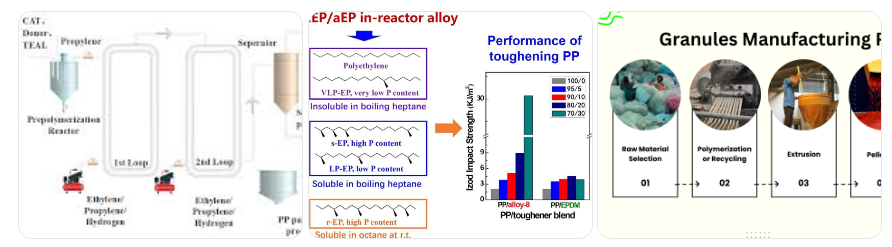
The production of PPCP involves creating a copolymer through controlled polymerization.
1. Raw Material Preparation
- Propylene gas and ethylene gas are purified.
- They are carefully measured, as the ratio affects strength, flexibility, and melting point.
2. Copolymerization Process
During polymerization:
- Propylene and ethylene are combined inside a reactor.
- A catalyst (usually Ziegler–Natta) initiates the reaction.
- Polymer chains form with embedded ethylene units, providing enhanced toughness.
This carefully controlled process creates impact-copolymer PP, known commercially as PPCP.
3. Processing Into Granules
Once polymerization is complete:
- The copolymer is extracted
- Stabilized
- Dried
- Cut into PPCP granules
Manufacturers then use these granules for injection molding or extrusion to create high-strength components.
Types of PPCP
1. Impact Copolymer PPCP
- Highest toughness
- Best for automotive and industrial applications
2. Random Copolymer (RCP) – Related Variant
Although not the same as PPCP, RCP is a softer, clearer copolymer used in packaging and household items.
Applications of PPCP

PPCP is used across multiple sectors due to its superior strength and durability. At Swami Polymers, our PPCP materials are chosen for:
Automotive Industry
- Battery cases
- Bumpers
- Air ducts
- Dashboards
- Trims & panels
Industrial Applications
- Storage crates
- Pallets
- Tool housings
- Machine components
- Chemical containers
Household & Consumer Products
- Buckets
- Furniture parts
- Containers
- Home appliance components
Electrical & Electronic
- Junction boxes
- Switch housings
- Cable management parts
Why Industries Prefer PPCP (And Why Swami Polymers Supplies It)
At Swami Polymers, PPCP is one of our most recommended materials because:
It delivers superior toughness compared to standard PP
It withstands heavy loads and impact
It performs well in low-temperature environments
It is cost-effective for mass production
It offers excellent chemical resistance
It supports consistent quality in molded products
We supply PPCP in various grades depending on the customer’s manufacturing needs.

Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is one of the most important and versatile synthetic plastic polymers used worldwide. At Swami Polymers, we supply high-quality PVC materials that support industries such as construction, electrical, packaging, and medical manufacturing. Because of its exceptional durability, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness, PVC continues to be a top choice for engineers, manufacturers, and product designers.
What Is PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)?
PVC is a thermoplastic polymer made by polymerizing vinyl chloride monomers (VCM). Due to its adaptable structure, PVC can be formulated to be rigid, semi-rigid, or flexible, making it suitable for hundreds of industrial and commercial applications.
Key Characteristics of PVC
- Excellent chemical resistance
- High durability and long service life
- Flame-retardant (self-extinguishing)
- Good electrical insulation properties
- Cost-effective and easy to process
- Can be rigid (uPVC) or flexible (Soft PVC)
- Weather and abrasion resistance
Because of these properties, PVC is one of the most widely used synthetic materials in the world, especially in construction and piping industries.
How PVC Is Made
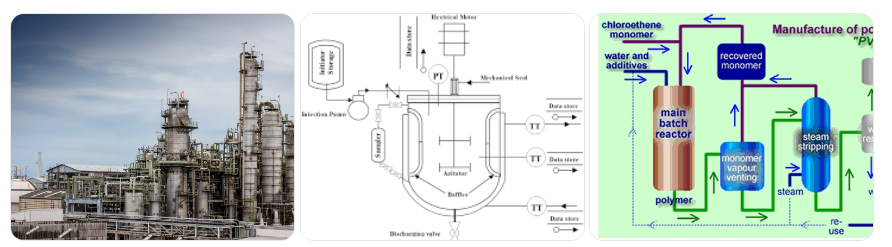
PVC production involves converting vinyl chloride monomers into a solid polymer through controlled polymerization.
1. Raw Material Preparation
PVC starts with ethylene (from crude oil or natural gas) reacting with chlorine to create vinyl chloride monomer (VCM).
Before polymerization, VCM is purified to remove impurities that may affect product quality.
2. Polymerization Process
The most common method is Suspension Polymerization, where:
- VCM is dispersed in water
- Special initiators trigger the polymerization reaction
- Under controlled temperature and pressure, VCM molecules link to form polyvinyl chloride polymer chains
After polymerization:
- The PVC resin is separated from water
- Dried
- Filtered
- Converted into PVC resin powder or granules
This raw PVC resin is the base material used for manufacturing thousands of products.
3. Formulation & Compounding
Pure PVC is rigid by nature.
To create different grades, additives are mixed such as:
- Plasticizers (for flexibility)
- Stabilizers
- Lubricants
- Fillers
- Color pigments
At Swami Polymers, we provide PVC materials tailored to meet specific performance requirements depending on the industry.
Types of PVC
1. Rigid PVC (uPVC)
- Used in pipes, doors, windows, fittings
- Strong and impact-resistant
- Weatherproof and corrosion-resistant
2. Flexible PVC
- Used in cables, hoses, flooring, medical tubes
- Soft, bendable, and lightweight
3. CPVC (Chlorinated PVC)
- Higher heat resistance
- Used for hot water pipes and industrial fluid handling
Applications of PVC Across Industries

PVC’s adaptability makes it one of the most used industrial materials. At Swami Polymers, our PVC materials support industries such as:
Construction & Infrastructure
- Water supply pipes
- Drainage systems
- Window frames
- Doors and profiles
- Roofing sheets
Electrical & Electronics
- Cable insulation
- Conduit pipes
- Connector covers
Packaging
- Shrink films
- Blister packs
- Food-grade wraps
Healthcare & Medical
- IV tubes
- Blood bags
- Medical containers
General Industrial Applications
- Hoses
- Conveyor belts
- Flooring materials
- Synthetic leather
Why PVC Is Preferred by Swami Polymers
At Swami Polymers, we choose PVC because it provides:
- Long lifespan with low maintenance
- Excellent performance in demanding environments
- High recyclability and sustainability potential
- Cost-effective manufacturing options
- Versatility across multiple sectors
Our PVC materials meet industry standards and support both small-scale and large-scale manufacturing needs.